HTML Introduction
HTML Editors »HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages.
What is HTML?
- HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language.
- It's the core language used to structure content on a web page.
- HTML uses a series of "elements" to enclose, or wrap, different parts of the content to make it appear or act a certain way.
- These elements can make a word a link, italicize text, or change the font size. For example, you can label content as "this is a heading," "this is a paragraph," or "this is a link."
A Simple HTML Document
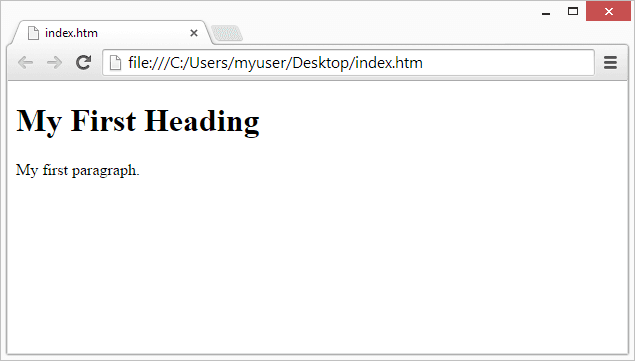
Below is an example of a very basic HTML document. You can copy this code and paste it into a file named index.html to see it in action.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>Example Explained
- The
<!DOCTYPE html>declaration defines that this document is an HTML5 document. - The
<html>element is the root element and wraps all the content on the entire page. - The
<head>element contains meta-information about the page, such as its title, which is not displayed on the page itself. - The
<title>element sets the title of the page, which appears in the browser tab. - The
<body>element contains all the content that you want to show to web users when they visit your page, such as headings, paragraphs, images, hyperlinks, tables, lists, etc. - The
<h1>element defines a large, important heading. - The
<p>element defines a paragraph of text.
What is an HTML Element?
An HTML element is typically defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag. The end tag is written like the start tag, but with a forward slash before the tag name.
<tagname> Content goes here... </tagname>The HTML element is everything from the start tag to the end tag:
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>| Start tag | Element content | End tag |
|---|---|---|
<h1> | My First Heading | </h1> |
<p> | My first paragraph. | </p> |
<br> | none | none |
Note: Some HTML elements, like <br> for a line break, have no content. These are called empty elements and do not have an end tag.
Web Browsers
The main job of a web browser (like Chrome, Firefox, or Safari) is to read HTML documents and display them as visual web pages. The browser does not display the HTML tags themselves, but uses them to interpret the structure and style of the content.
HTML Page Structure
Below is a simple visualization of how an HTML page is structured hierarchically:
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
HTML History
Since the beginning of the World Wide Web, HTML has evolved through many versions. This tutorial follows the latest HTML5 standard.
| Year | Version |
|---|---|
| 1989 | Tim Berners-Lee invented www |
| 1991 | Tim Berners-Lee invented HTML |
| 1993 | Dave Raggett drafted HTML+ |
| 1995 | HTML Working Group defined HTML 2.0 |
| 1997 | W3C Recommendation: HTML 3.2 |
| 1999 | W3C Recommendation: HTML 4.01 |
| 2000 | W3C Recommendation: XHTML 1.0 |
| 2008 | WHATWG HTML5 First Public Draft |
| 2012 | WHATWG HTML5 Living Standard |
| 2014 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5 |
| 2017 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5.1 2nd Edition |
| 2017 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5.2 |
Test Yourself with an Exercise
What does HTML stand for?